The Software Development Life Cycle and Prototyping
Overview
The software development life cycle is comprised of two parts: a description of the phases of development and the order in which the phases are to be carried out.
The General Model of the SDLC
The general model of software development can be split into 5 distinct phases.
The specification requirements are an essential step in the development cycle. At this stage, the designers, users and programmers should all be involved. After this stage, everyone should be aware of:
- What functions the software will perform.
- What the UX will be like.
- What data the software will access, produce and store.
- How the data will be processed.
By the end of this phase, a specification document should be drawn up that can be referred to throughout the development process.
The design stage is usually carried out by software architects. This is often accomplished using flowcharts to detail the flow of data through the software. At this stage, mock-ups of the UI are also often created.
At the implementation stage the code is written. The programmers will accomplish this using the design that was provided by the software architects in the design stage.
During the testing stage the software is tested against the specification. Unit tests are used to test individual elements of the software, while software tests are used to test the software as a whole.
At the evolution stage, software is upgraded. This can happen for a number of different reasons:
- Flaws or bugs in the original software are discovered.
- Security update are carried out due to previously unknown threats.
- The customer requirements may change.
- There may be hardware changes which need to be carried out.
Models of Software Development
There are four major SD models: the waterfall model; the incremental model; the spiral model; and the v-shaped model.
Waterfall Model
In the waterfall model, there are the usual 5 stages of development. However, the development should not move to the next step until the previous step has been fully completed and verified.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Works well for smaller projects where requirements are very well understood | High amounts of risk and uncertainty |
| Easy to manage due to the rigidity of the model | No working software is produced until late in the development cycle |
Incremental Model
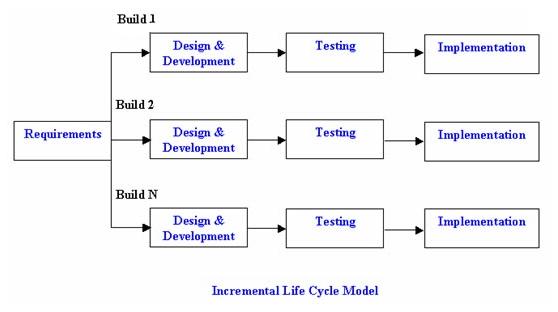
In the incremental model the requirements are divided into various builds, thus multiple development cycles occur. Each cycle is divided into more easily managed modules, which all go through the phases of design, development, testing and implementation.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Generates working software quickly and early in the development cycle | Needs good planning and design to work effectively |
| Easier to test and debug code in a smaller iteration | Needs a “clear and complete” definition of the program before it can be split incrementally |
Spiral Model
The spiral model is split into the four stages of planning, risk analysis, development and evaluation. The projects repeatedly passes through these steps in iterations until all issues are resolved.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| High amount of risk analysis, so good for higher-risk projects | Can be a costly model to use |
| Software is produced early in the development cycle | Success is heavily reliant on the risk analysis stage of development |
V-Shaped Model

Similarly to the waterfall model, the V-shaped model can only continue onto the next step when the previous step is fully completed and verified. However, the testing of the product is planned in parallel to the design of the product with a corresponding phase of development, making the V-shaped model more similar to test-driven development or TDD.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Testing is planned before the software is written, saving a lot of time | Very rigid and has little flexibility |
| Example of proactive defect tracking, where defects are found early on | If any changes happen midway, then the test documents and the requirement documents have to be updated as well |
Prototyping
A prototype is an early model or release of software built to test a concept or to act as something to be replicated or learned from. They typically allow a customer to evaluate a product or feature of a proposed software solution, rather than relying on interpretations of designs.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Prototypes help evaluate whether the developed software matches the specification | The prototype may be perfect, but are unable to be scaled into a full solution |
| They allow the client to provide feedback on software features, even if the full solution is incomplete | Prototyping can be excessively long if it is not done correctly - it should be quick to be effective |
| They assist in producing a product that more closely matches the client’s needs. |